Fastener definition
It is the general term of a kind of mechanical parts used to fasten and connect two or more parts (or components) into a whole. It is also called "standard part" in the market.
It usually includes: bolts, studs, screws, self tapping screws, wood screws, nuts, pins and keys, washers, retainer rings, rivets, assemblies and connecting pairs.
Classification of fasteners
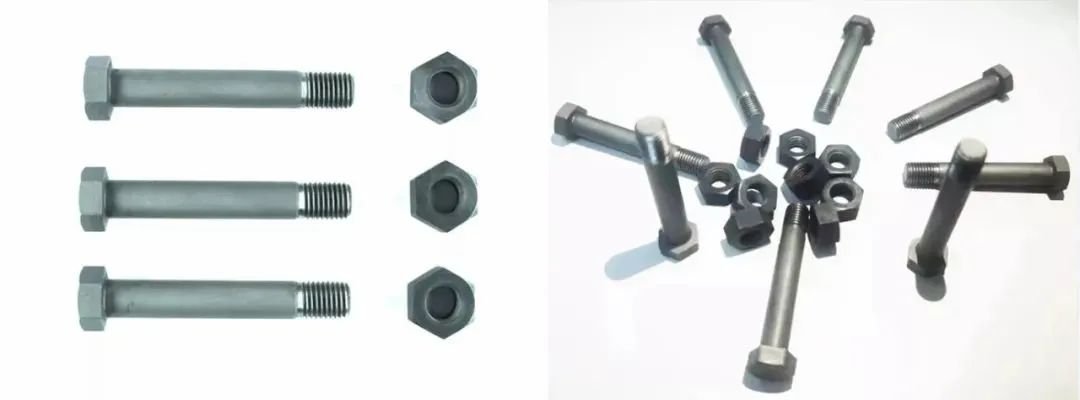
Bolt: a kind of fastener composed of head and screw (cylinder with external thread). It is usually matched with nut or screw hole to connect two objects with through holes or screw holes;
Stud: a type of fastener with no head and only external threads at both ends;
Screw: it is also a kind of fastener composed of head and screw. It is usually divided into: mechanical screw, set screw and special-purpose screw;
Nut: with internal thread hole, the shape is generally flat hexagon or cylindrical. It is used to connect two objects together with studs and bolts to form a whole.
Self tapping screw: this kind of screw has high hardness and can be directly screwed into the component.
Pin and key: mainly used for part positioning, part connection, fixing parts and transmitting power.
Washer: divided into flat circular ring and elastic washer
Retaining ring: it is used to install in the shaft groove or hole groove of the machine and equipment, so that the two parts will not move axially;
Rivet: a kind of fastener composed of head and shank;
Assembly and connection pair: assembly refers to a type of fasteners supplied in combination. Connection pair refers to a group of parts supplied by a combination of special bolts, nuts and washers.
Thread definition
Introduction to fasteners
Definition of thread: thread is a shape with uniform spiral protrusions on the section of the outer or inner surface of a solid.

Thread classification can be divided into three categories according to its structural characteristics and uses:
Common thread: the tooth shape is triangular, which is used to connect or fasten parts. Ordinary thread can be divided into coarse thread and fine thread according to pitch, and fine thread has high connection strength.
Transmission thread: the tooth shape includes trapezoid, rectangle, saw and triangle.

Sealing thread: used for sealing connection, mainly including pipe thread, taper thread and taper pipe thread.

Types of threaded fasteners
Hexagon head bolt, stud, hexagon nut, hexagon slotted nut
Hexagon socket head cap screws slotted head cap screws slotted countersunk head screws set screws
Flat washer, spring washer, tab washer for round nut, round nut
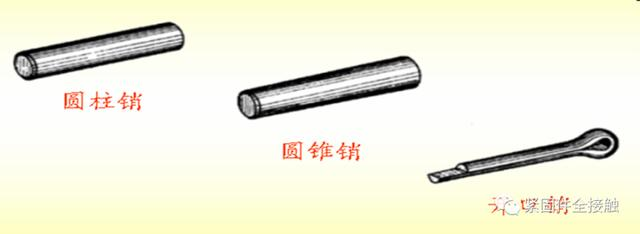
Type of pin
 Type of key
Type of key
There are many types of keys. The commonly used keys include ordinary flat keys, semicircular keys, hook head wedge keys, etc., of which ordinary flat keys are the most common. The key is also a standard part.
Flat key, semicircular key, hook head wedge key
Identification of bolts

Performance level
Mark: Hexagon head bolts and screws (thread diameter ≥ 5mm). It is required to mark the top surface of the head with convex or concave characters, or the side surface of the head with concave characters: including performance grade and factory logo. The strength grade marking code for steel is composed of two numbers separated by "·". The meaning of the number before "·" in the marking code indicates the nominal tensile strength, for example, "4" in grade 4.8 indicates 1 / 100 of the nominal tensile strength 400MPa. The meaning of "·" and the digital part after the point in the mark code indicates yield strength ratio, that is, the ratio of nominal yield point or nominal yield strength to nominal tensile strength. For example, the yield point of grade 4.8 product is 320MPa, and its yield strength ratio is 0.8.
2. Grade: the mechanical performance grade of metric bolts can be divided into 10 performance grades: 3.6, 4.6, 4.8, 5.6, 5.8, 6.8, 8.8, 9.8, 10.9 and 12.9. (see figure below)
Mechanical property grade and material selection of metric bolts
Bolt production process
1. Process flow (cold heading) ●
Disk element annealing pickling wire drawing (annealing) cold heading
Packaging surface treatment heat treatment rubbing (rolling) teeth
Introduction to key processes
1. Annealing
Purpose:
Heat the wire to an appropriate temperature, keep it for a certain time, and then slowly cool it to adjust the crystal structure, reduce the hardness, and improve the processability of the wire at room temperature.
Operation process:
Feeding: lift the products to be processed into the furnace, and pay attention to the tight cover of the furnace. Generally, one furnace can be used at the same time
I sorted several volumes.
Temperature rise: slowly (about 3-4 hours) raise the temperature in the furnace to the specified temperature.
Thermal insulation: wire 1018 is kept at 680 ℃ - 715 ℃ for 4-6h, and wire 10B21 is kept at 740 ℃
-760 ℃ for 5.5-7.5h.
Cooling: slowly reduce the temperature in the furnace (about 3-4 hours) to below 550 ℃, and then cool down to normal temperature with the furnace
Quality control:
Hardness: the hardness of 1018 and 1022 wires after annealing is hv120-170, and the hardness of medium carbon wires after annealing is hv120-180.
Appearance: the surface shall be free of oxide film and decarburization.
2. Pickling
Purpose:
The oxide film on the wire surface is removed, and a phosphate film is formed on the metal surface to reduce the abrasion of tools and dies during wire drawing, cold pier or forming.
Operation process:
Pickling: immerse the whole disc into three hydrochloric acid tanks with a concentration of 20-25% at room temperature for several minutes, with the purpose of removing the oxide film on the wire surface.
Clean water: remove the hydrochloric acid corrosion products on the wire surface.
Oxalic acid: increase the activity of metal to make the film produced in the next process more compact.
Phosphating treatment: immerse the disc element in phosphate, contact the steel surface with the chemical treatment solution, dissolve the steel to form insoluble compounds (such as zn2fe (po42 · 4H2O), adhere to the steel surface to form a clear water film: remove the residues on the surface of the film.
Lubricant: because the friction coefficient of phosphate film is not very low, it can not give sufficient lubricity during processing, but it reacts with metal soap (such as sodium soap) to form a hard metal soap layer, which can increase its lubricating performance.
3. Wire drawing
Purpose: cold draw the coil element to the required wire diameter. In practice, for some products, it can be divided into two stages: rough drawing (shelling) and fine drawing.
4. (cold and hot heading) head forming
Purpose: to form the bolt head or nut by cold upsetting (or hot forging) of wire to achieve the shape and length (or thickness) of semi-finished products.
5. Screw forming
Purpose: rolling or tapping the formed semi-finished products to achieve the required threads. Generally speaking, for bolts (screws), it is called thread rolling, for large diameter bolts or thread strips, it is called rolling, and for nuts, it is called tapping.








